Oral cancers are part of a group of cancers commonly referred to as head and neck cancers, and of all head and neck cancers, they comprise about 85% of that category. Brain cancer is a cancer category unto itself and is not included in the head and neck cancer group. With more than half a million cases a year behind it and with a mortality of about 330,000 people. The high mortality rate is due in most cases to a late diagnosis. When any of the characteristic symptoms are observed, metastasis has usually already occurred and life expectancy is greatly reduced. In this article, we will discuss the symptoms and risk factors of oral cancers.
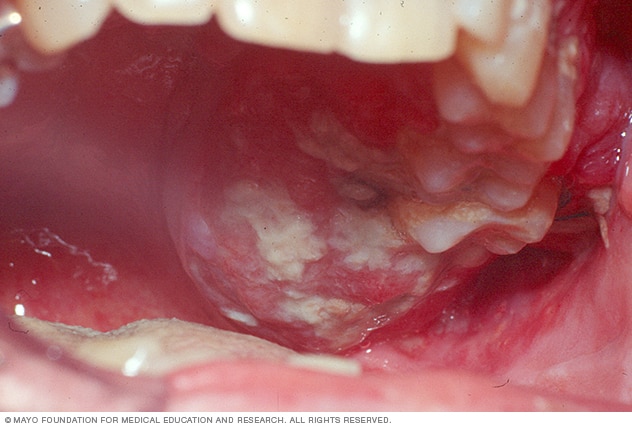
Oral Cancer.Photo credit Mayo Clinic
Symptoms of oral cancer
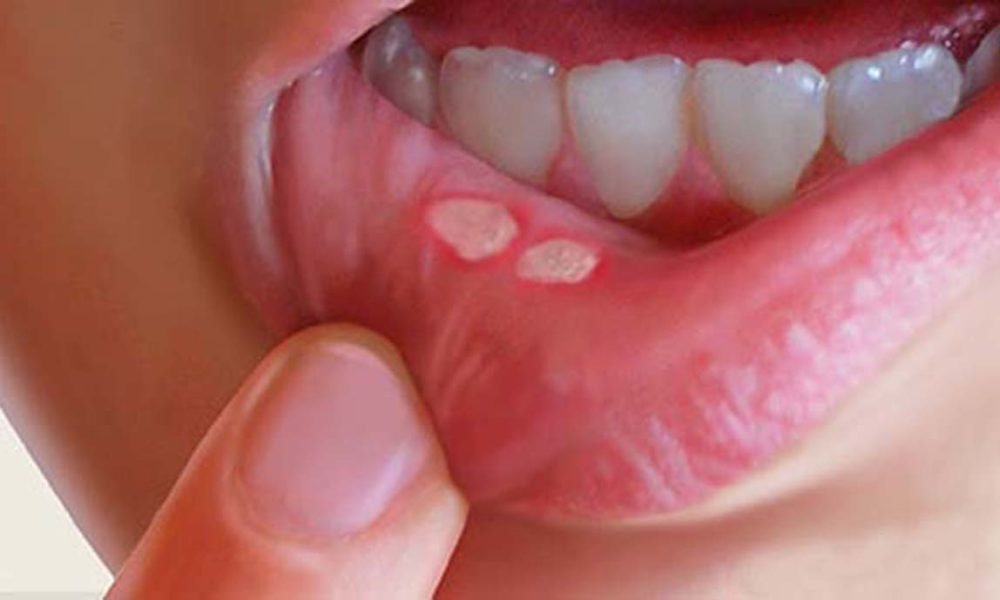
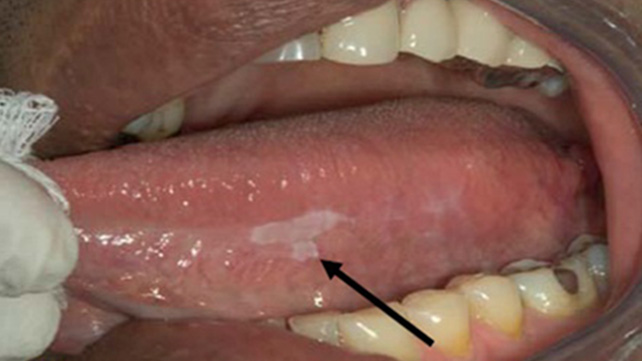
The most widespread indicator of oral cancer is a sore or an ulcer in the mouth that does not heal. Another frequent sign is a pain in the mouth that does not heal. Additional symptoms and warning signs of oral cancers consist of:
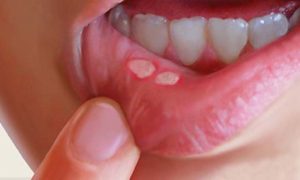
- white patches (leukoplakia), red patches (erythroplakia), or mixed red and white
patches (erythroleukoplakia) on the lips or in the mouth - a lump on the lips, in the mouth, or on the tongue
- thickening of the inner cheek lining
- hemorrhage in the mouth
- weak teeth
- incoherent speaking
- inflamed salivary glands
- inflamed lymph nodes in the neck
- lack of sensation over the tongue or lips
- inflammation of the jaw
- voice alterations
- ache when swallowing

Oral Cancers: Risk Factors
Modifying or avoiding the following key risk factors can help prevent cancer:
- Tobacco
Not only does it increase the risk of oral cancer, but other types of cancer such as lung cancer. Tobacco wreaks havoc in the mouth, whether smoked or chewed, and cancer of the cheeks, lips, and gums is one of the most serious problems it causes.
- Alcohol
7 out of 10 patients diagnosed with oral cancer consume alcohol. According to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) two or more alcoholic drinks, a day for men can be considered heavy drinkers and for women, the amount is more than one alcoholic drink a day. If alcohol is consumed with tobacco, the chances of contracting oral cancer multiply.
- HPV
The Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection made up of more than 200 viruses, and about 40 are those that are transmitted by this route. Low and high risk are differentiated from the latter, the latter being those that cause cancer. According to the data, head and neck cancers (especially those that occur on the back of the tongue in or around the tonsils) associated with HPV have increased dramatically since 2008. The dentist can help detect oral cancer early attending frequently to carry out check-ups. It is also important to use protection in sexual intercourse since, as we have mentioned, it is a virus that is transmitted by this route and, given its incidence, a vaccine has also been launched for boys and girls between 11 and 12 years old.
Other risk factors
Other influencing factors are gender and sex. Men are reportedly more likely to develop oral cancer due to more alcohol and tobacco use. Regarding age, they are usually detected after 55 years of age, but in cases of oral cancer associated with HPV, they are diagnosed more often in young people.
Following a healthy diet is also important. If we do not eat properly and we lack nutrients, the risk of developing oral cancer, among other complications, also increases. This lack of nutritious food can be highly detrimental to our general health.
Follow Dr. Pascal Terjanian blog for more helpful dental articles.